Learn More
Abnova™ Human B4GALT7 Partial ORF (NP_009186.1, 51 a.a. - 140 a.a.) Recombinant Protein with GST-tag at N-terminal
Description
This gene is one of seven beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase (beta4GalT) genes. They encode type II membrane-bound glycoproteins that appear to have exclusive specificity for the donor substrate UDP-galactose; all transfer galactose in a beta1,4 linkage to similar acceptor sugars: GlcNAc, Glc, and Xyl. Each beta4GalT has a distinct function in the biosynthesis of different glycoconjugates and saccharide structures. As type II membrane proteins, they have an N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence that directs the protein to the Golgi apparatus and which then remains uncleaved to function as a transmembrane anchor. By sequence similarity, the beta4GalTs form four groups: beta4GalT1 and beta4GalT2, beta4GalT3 and beta4GalT4, beta4GalT5 and beta4GalT6, and beta4GalT7. The enzyme encoded by this gene attaches the first galactose in the common carbohydrate-protein (GlcA-beta1,3-Gal-beta1,3-Gal-beta1,4-Xyl-beta1-O-Ser) linkage found in proteoglycans. Manganese is required as a cofactor. This enzyme differs from the other six beta4GalTs because it lacks the conserved beta4GalT1-beta4GalT6 Cys residues and it is located in cis-Golgi instead of trans-Golgi. Two single-nucleotide mutations were identified from a patient with the progeroid type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. [provided by RefSeq]
Specifications
Specifications
| Accession Number | NP_009186.1 |
| For Use With (Application) | Antibody Production, ELISA, Protein Array, Western Blot |
| Formulation | 50mM Tris-HCI, 10mM reduced Glutathione, pH=8.0 in the elution buffer. |
| Gene ID (Entrez) | 11285 |
| Molecular Weight (g/mol) | 35.64kDa |
| Name | B4GALT7 (Human) Recombinant Protein (Q02) |
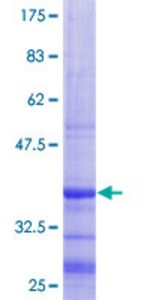
| Quality Control Testing | 12.5% SDS-PAGE Stained with Coomassie Blue. |
| Quantity | 10 μg |
| Immunogen | LSCSGDVARAVRGQGQETSGPPRACPPEPPPEHWEEDASWGPHRLAVLVPFRERFEELLVFVPHMRRFLSRKKIRHHIYVLNQVDHFRFN |
| Storage Requirements | Store at -80°C. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Show More |
Your input is important to us. Please complete this form to provide feedback related to the content on this product.