Goat Secondary Antibodies
Browse our extensive range of goat secondary antibodies targeting various species. Choose from monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies, available in conjugated, unconjugated, and other forms, suitable for a wide range of applications to meet your specific needs.
Useful Links
Save Now - Exclusive Deals
Product Code 15290371
Product Code 18165601
Product Code 11545075
Product Code 10286672
Product Code 10727464
Product Code 11505075
Product Code 11859140
Must Have
Product Code 10157014
Product Code 10694383
Product Code 18189730
Complete Your Order - Great Deals
FAQ
Goat secondary antibodies are antibodies produced in goats that bind specifically to primary antibodies from another species (e.g., rabbit, mouse). The goat's immune system recognizes these foreign IgGs and produces antibodies against them. The resulting antibodies are highly specific to the IgG of the species they were raised against. For example, Goat anti-rabbit: Binds to rabbit IgG. Goat anti-mouse: Binds to mouse IgG. Goat anti-human: Binds to human IgG.
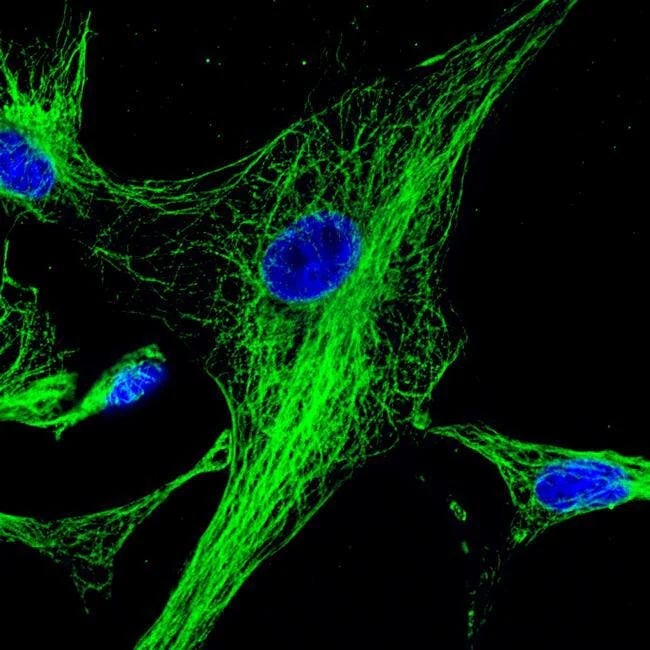
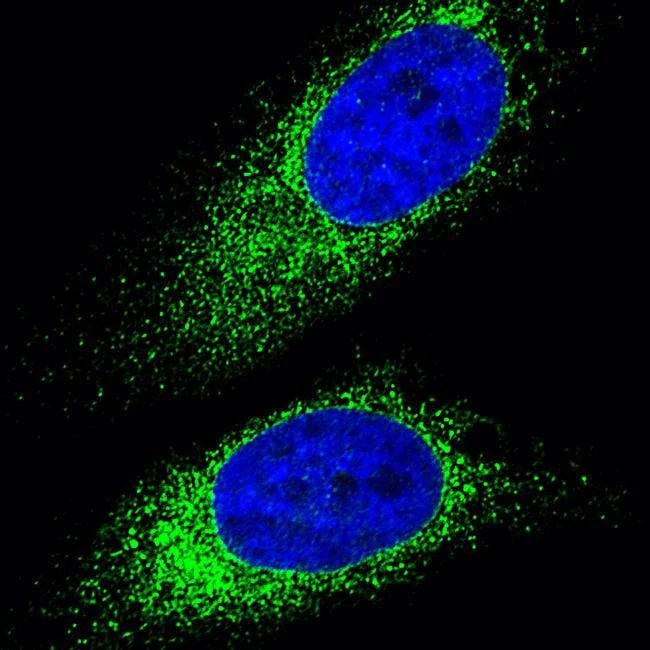
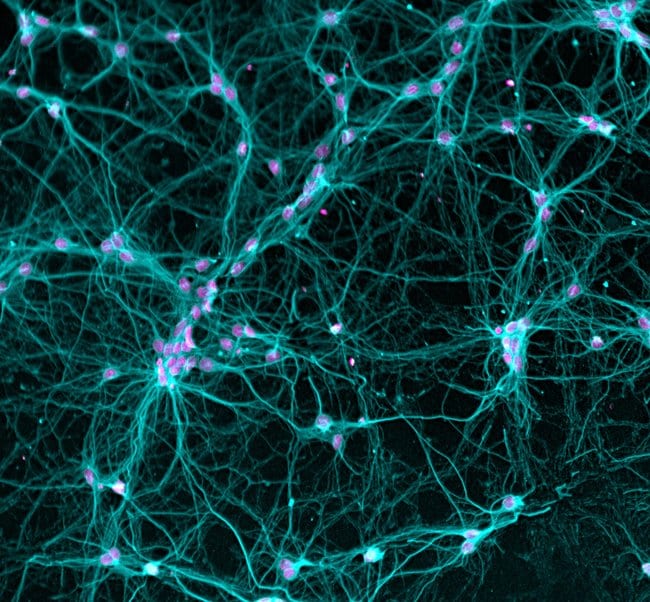
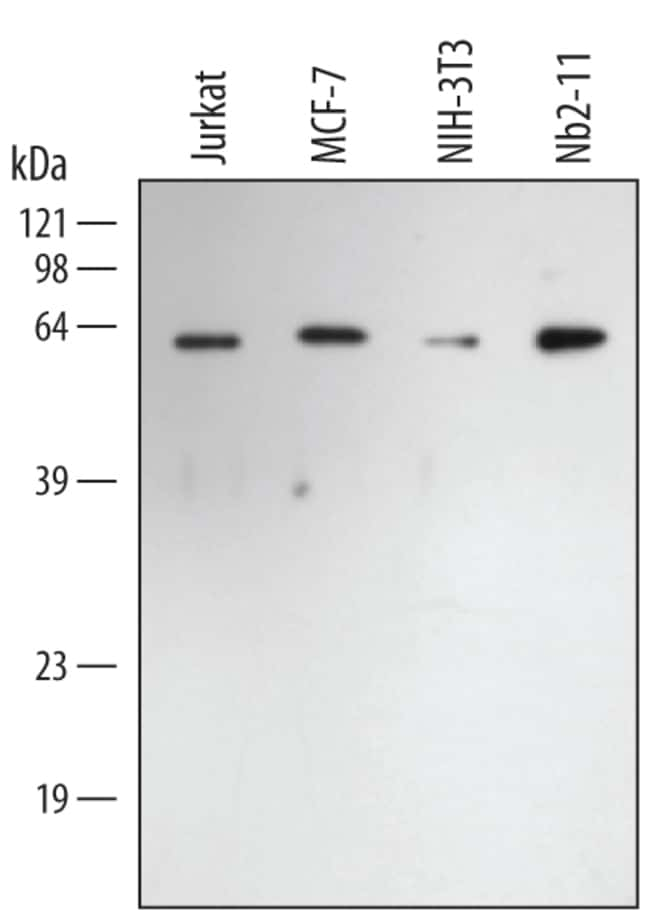
They are used in various immunoassays (Western blotting, ELISA, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence) to detect and visualize target antigens. These antibodies are often conjugated to reporter molecules like enzymes (HRP), fluorophores (FITC), or biotin for detection.
The number of times you can use a secondary antibody depends on the antibody's stability, storage conditions, and the specific application. Typically, secondary antibodies can be used multiple times if they are stored properly usually at -20°C for long-term storage or 4°C for short-term, and if they have not been contaminated. Using sterile techniques and aliquoting the antibody to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles can extend its usability. The number of uses can also depend on the type of experiment (e.g., Western blotting, immunohistochemistry) and the concentration required. For Western blotting, a secondary antibody can often be reused multiple times, sometimes up to 10-20 times, if stored correctly and used at the recommended dilution. Always refer to the manufacturer's guidelines for the most accurate information.
When selecting goat secondary antibodies, consider the following five factors:
- Species Specificity: Ensure the secondary antibody is specific to the primary antibody's host species (e.g., goat anti-rabbit for rabbit primary antibodies).
- Conjugation: Choose the appropriate conjugate for your detection method, such as enzymes (HRP, AP), fluorophores (FITC, Alexa Fluor), or biotin.
- Affinity and Purity: Select antibodies with high affinity and purity to ensure specific binding and minimal background noise.
- Application Compatibility: Ensure the secondary antibody is suitable for your specific application (e.g., Western blotting, ELISA, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence).
- Validation and Reviews: Check for validation data and reviews to confirm the antibody's reliability and performance in similar experiments.